“Introduction to SQL for BigQuery and Cloud SQL”
Daftar Isi
Pengantar
SQL (Structured Query Language) adalah bahasa standar untuk operasi data yang memungkinkan Anda mengajukan pertanyaan dan mendapatkan wawasan dari kumpulan data terstruktur. Ini umumnya digunakan dalam manajemen basis data dan memungkinkan Anda melakukan tugas seperti penulisan catatan transaksi ke dalam basis data relasional dan analisis data berskala petabyte.
Praktikum
Task 1. The basics of SQL
Databases and tables
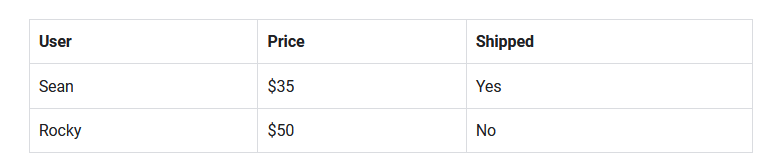
SELECT and FROM
Contoh command :
SELECT USER FROM example_table
SELECT USER, SHIPPED FROM example_table
WHERE
SELECT USER FROM example_table WHERE SHIPPED='YES'
Task 2. Exploring the BigQuery console
- Klik Navigation menu > BigQuery
- Klik Done
Uploading queryable data
- Click on + ADD DATA
- Choose Star a project by name > Star a project
- Enter project name as bigquery-public-data
- Click the STAR
- In the search bar, enter London Bicycles Hires and click VIEW DATASET
- You now have access to the following data
Google Cloud Project → bigquery-public-data
Dataset → london_bicycles- Click on the london bicycles dataset to reveal the associated tables
Table → cycle_hire
Table → cycle_stationsIn this lab we will use the data from cycle_hire. Open the cycle_hire table, then click the Preview tab. Your page should resemble the following:
Running SELECT, FROM, and WHERE in BigQuery
- Copy and paste the following command into the query EDITOR:
SELECT end_station_name FROM `bigquery-public-data.london_bicycles.cycle_hire`;- Klik Run
SELECT * FROM `bigquery-public-data.london_bicycles.cycle_hire` WHERE duration>=1200;Task 3. More SQL Keywords: GROUP BY, COUNT, AS, and ORDER BY
GROUP BY
SELECT start_station_name FROM `bigquery-public-data.london_bicycles.cycle_hire` GROUP BY start_station_name;- klik Run
COUNT
SELECT start_station_name, COUNT(*) FROM `bigquery-public-data.london_bicycles.cycle_hire` GROUP BY start_station_name;AS
SELECT start_station_name, COUNT(*) AS num_starts FROM `bigquery-public-data.london_bicycles.cycle_hire` GROUP BY start_station_name;ORDER BY
SELECT start_station_name, COUNT(*) AS num FROM `bigquery-public-data.london_bicycles.cycle_hire` GROUP BY start_station_name ORDER BY start_station_name;SELECT start_station_name, COUNT(*) AS num FROM `bigquery-public-data.london_bicycles.cycle_hire` GROUP BY start_station_name ORDER BY num;SELECT start_station_name, COUNT(*) AS num FROM `bigquery-public-data.london_bicycles.cycle_hire` GROUP BY start_station_name ORDER BY num DESC;Task 4. Working with Cloud SQL
Exporting queries as CSV files
- Run
SELECT start_station_name, COUNT(*) AS num FROM `bigquery-public-data.london_bicycles.cycle_hire` GROUP BY start_station_name ORDER BY num DESC;- In the Query Results section click SAVE RESULTS > CSV(local file). This initiates a download, which saves this query as a CSV file. Note the location and the name of this downloaded file—you will need it soon.
Upload CSV files to Cloud Storage
- Open Navigation menu > Cloud Storage > Buckets, and then click CREATE BUCKET
- Create bucket
- Click UPLOAD FILES and select the CSV that contains
start_station_namedata. - Then click Open. Repeat this for the
end_station_namedata. - Rename your
start_station_namefile by clicking on the three dots next to on the far side of the file and click rename. Rename the file tostart_station_data.csv. - Rename your
end_station_namefile by clicking on the three dots next to on the far side of the file and click rename. Rename the file toend_station_data.csv.
Task 5. Create a Cloud SQL instance
- select Navigation menu > SQL
- Click CREATE INSTANCE > Choose MySQL .
- Enter instance id as qwiklabs-demo
- Enter a secure password in the Password field (remember it!)
- Select the database version as MySQL 5.7.
- Set the Multi zones (Highly available) field as
- Click CREATE INSTANCE.
- Click on the Cloud SQL instance. The SQL Overview page opens.
Task 6. New queries in Cloud SQL
CREATE keyword (databases and tables)
https://shell.cloud.google.com/?show=terminal
gcloud config set project [PROJECT_ID]Create a database in Cloud Shell
gcloud auth login --no-launch-browser
gcloud config set project [PROJECT_ID]
gcloud sql connect qwiklabs-demo --user=root --quiet
CREATE DATABASE bike;
USE bike;
CREATE TABLE london1 (start_station_name VARCHAR(255), num INT);
USE bike;
CREATE TABLE london2 (end_station_name VARCHAR(255), num INT);
SELECT * FROM london1;
SELECT * FROM london2;Upload CSV files to tables
- In your Cloud SQL instance page, click IMPORT.
- In the Cloud Storage file field, click Browse, and then click the arrow opposite your bucket name, and then click
start_station_data.csv. Click Select. - Select CSV as File format.
- Select the
bikedatabase and type in “london1” as your table. - Click Import
Penutup
Sahabat Blog Learning & Doing demikianlah penjelasan mengenai Introduction to SQL for BigQuery and Cloud SQL. Semoga Bermanfaat . Sampai ketemu lagi di postingan berikut nya.














